Top Factors to Assess When Evaluating Graphic Designer Portfolios!
- Visruth Devadas
- July 15, 2024
- 8 Minute Read

Graphic design is a vast field in which professionals garner expertise in website design, logo design, interior decoration, and more. Visuals are an enticing way to enhance your business, whether through product images, social media profiles, attractive landing pages, etc.
Research by Sproutworth shows that businesses that portray articles with images can get 94% more views, and videos on landing pages can enhance lead conversions by 80%. Moreover, 65% of businesses believe visual assets can help business marketers communicate their brand story.
As a business, hiring graphic designers from elite platforms is integral to reaching your target audience and enhancing your brand value. When hiring an expert, one of the most crucial factors to consider is the graphic designer’s portfolio. A well-crafted portfolio is a critical tool that is more like a visual resume of the candidate.
Let us explore the significance of a graphic designer’s portfolio in this guide and discover key elements that businesses must look into before hiring a graphic designer!
Understanding the Role and Scope
A graphic designer’s portfolio highlights the designer’s creativity, technical skills, and professional experience.

What to Expect from a Graphic Designer’s Portfolio
When scrutinizing the best graphic design portfolios, you can expect:
- Project Samples featuring a variety of projects, that show the designer’s versatility
- Examples that emphasize the quality of work
- Case studies that outline the design process, challenges faced, solutions implemented, and outcomes
- A consistent visual style and conceptual clarity
Different Types of Portfolios
There are different types of graphic designer portfolios that you can come across:

1. Print Portfolios
This portfolio is in the physical form that highlights the printed versions of the designer’s work. This can include brochures, business cards, posters, etc. Such portfolios can help you during the meeting or interview process. You also get an idea about the tangible experience of the designer’s ability to handle print production.
2. Digital Portfolios
Digital portfolios are an online collection of design-related work that can be found on a personal website, social media platform, or other web platforms like Uplers, Dribbble, or Adobe Portfolio. They are easily accessible and can showcase a variety of interactive elements.
3. Mixed Media Portfolios
These portfolios combine the tangible experience of print and the convenience of digital media.
What to Include in a Graphic Designer Portfolio
Various elements that you must look out for when scrutinizing the best graphic designer portfolios are:
- Motion Graphics with graphic design to create engaging content
- Videos in the form of advertisements, promotional content, or explainers that highlight versatility
- Original Illustrations used in branding, editorial design, and digital media
- The animation ranges from simple GIFs to complex character animations
- Product Design including the design of physical products, packaging, user experience, etc.
- Ad Campaigns, including print ads, social media graphics, videos, and more
- Storyboards and visual representations of how a story or message will unfold using effective storytelling skills
Key Elements to Look for in a Portfolio
Here are some of the most critical elements to consider when going through a graphic designer’s portfolio:
1. Design Diversity and Versatility
Look for a variety of projects that showcase the designer’s ability to work across different styles. Check the types of graphic designing he has ventured into like print design, digital design, branding, log-making, etc. The portfolio should show how the designer has handled client needs and project scopes.
A plus point would be if the portfolio includes work from various industries, which means he can cater to different market segments and target audiences.
2. Quality of Work and Attention to Detail
Here are some key aspects that you must look into to understand the quality of a graphic designer’s work:
- How comfortably he can work with design tools and software
- His understanding of design principles such as color theory, typography, and composition
- Attention to detail in every project
- Choice of fonts and colors for the alignment and spacing
- The overall presentation of the portfolio
3. Creativity and Innovation in Design Solutions
The portfolio should showcase original ideas and creative approaches to design challenges. This creativity can be shown using the following:
- Evidence of how the designer approaches and solves specific design problems
- Detailed case studies or descriptions of the design process
- Innovative design solutions
- Strong conceptual thinking
- Creative concepts that effectively communicate the brand identity
Technical Proficiency and Tools
When assessing a graphic designer’s portfolio, technical proficiency and the effective use of tools should be critically assessed to understand a designer’s capability and potential. Here are the key aspects to consider:
1. Software Skills and Proficiency Levels
The portfolio should depict the designer’s proficiency with industry-standard software. Look for expertise in Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign, and knowledge of other tools such as Adobe After Effects, Adobe XD, or Sketch.
- Look for proficiency in 3D Design Software.
- Level of Expertise: The portfolio should reflect the designer’s skill level, whether he is a beginner or an advanced designer.
- Certification and Training: Besides highlighting the basic educational qualifications, a solid portfolio should contain information about formal training, certifications, or courses completed in relevant software.
2. Understanding of Design Principles and Techniques
Fundamental design principles and techniques that should be highlighted within the designer’s portfolio are:
- Color Theory: The ability to create visually appealing color schemes
- Typography, including font selection and creative use of type
- Composition and Layout to create well-organized designs
- Branding and Identity, including logos, business cards, and other brand assets
- Illustration and Digital Art that enhance the overall design
- Interaction and User Experience Design
For example
Check out the interactive design portfolio for Peter Tarka.

This outstanding portfolio attracts businesses because of the captivating 3D motion graphics, vector graphics, and the elaborate experience of the designer, who has showcased his work with brands like Spotify, Google, and LG.
Assessing Design Process and Problem-Solving Skills
A strong graphic designer portfolio helps you assess the designer’s process and approach to solving design challenges. This can be portrayed through case studies and project descriptions.
1. Case Studies and Project Descriptions
Detailed Case Studies should contain:
- A brief overview of the project, including the client, the project’s goals, and the designer’s role
- Context about the project’s background, target audience, and market
- Detailed documentation of the design process, from initial research to final execution
- A clear project description, including the project’s objectives and goals, challenges or constraints faced during the project, solutions implemented to address these challenges, and the outcomes achieved
2. Approach to Design Challenges and Solutions
Another key feature to gauge from a portfolio is how the experts approach challenges and solutions. Here are some tips:
- Look for evidence, such as reviews or market analyses, that shows his deep understanding of the problem at hand.
- Focus on user-centered design principles, which demonstrates how the designer considered the client’s needs and behaviors.
- Look for the ideation phase, which reflects his creativity and ability to generate multiple ideas.
- Check feedback loops, iterations, and client consultations.
Client Collaboration and Communication
Effective client collaboration and communication are critical components of a successful graphic design career. A portfolio should reflect these skills.
1. Ability to Understand and Interpret Client Briefs
The portfolio should demonstrate that the designer can accurately interpret and understand client briefs. Examples should show how the designer’s work aligns with the client’s objectives and how he considers the specifics of each client rather than using a standard method. So, what to include in a graphic designer portfolio? Here is a list of significant inclusions:
Case Studies Highlighting Client Collaboration
Case studies should include information about initial client meetings and how the designer gathered and clarified requirements. Other important inclusions are:
Ongoing feedback and iterations:
- Examples of how the designer incorporated client feedback and made adjustments
- Testimonials and client feedback provide valuable insights into a designer’s skills and abilities
- Ability to understand branding guidelines
2. Communication Skills and Responsiveness
The portfolio should reflect the designer’s ability to communicate ideas clearly and concisely. This can be gauged through:
- Written descriptions
- Visual presentations
- Verbal interactions.
- Presentations
- Pitch decks
- Client correspondence
- Responsiveness and Professionalism
For example:
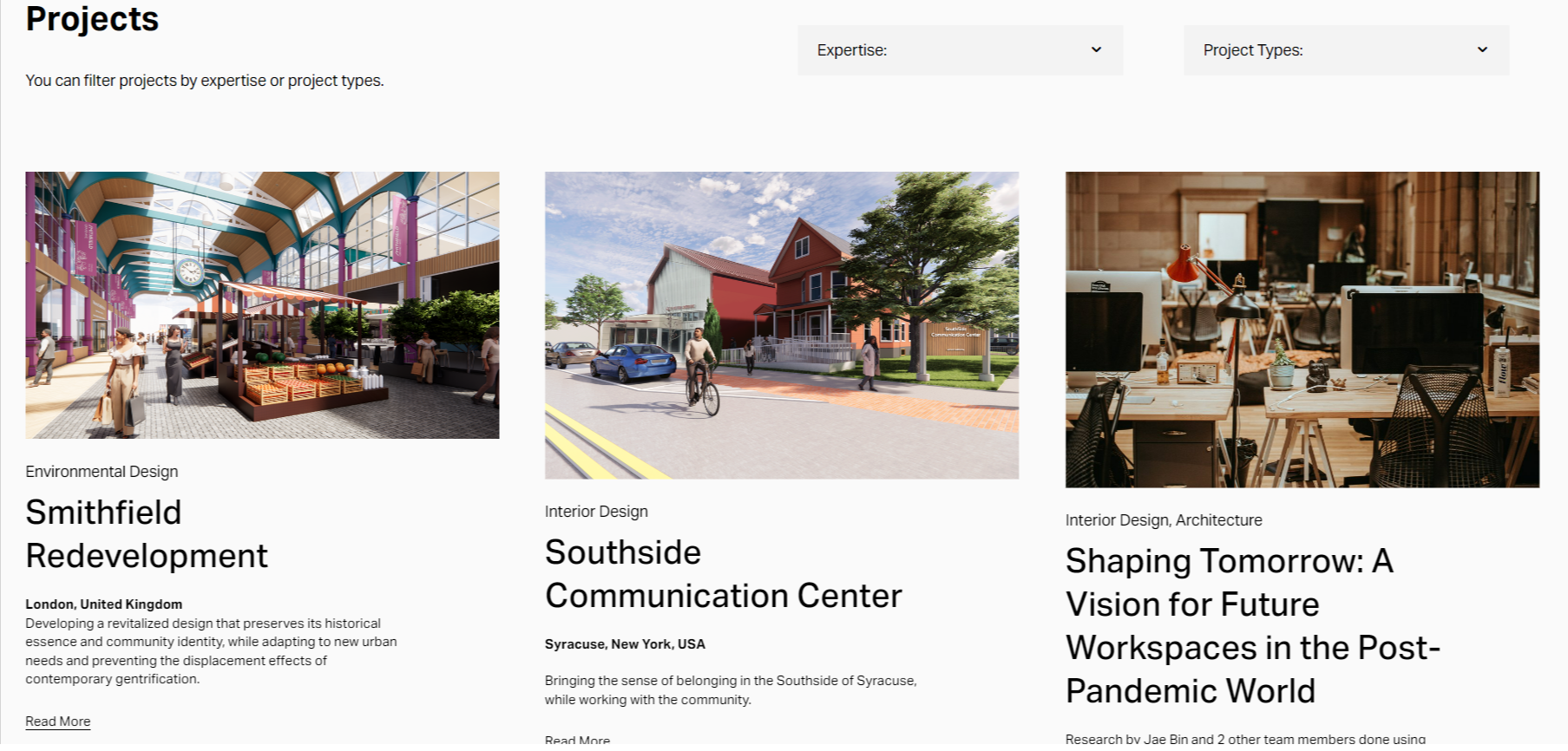
Jae Bin Lee has designed his portfolio just like a chapter book. It has a detailed table of contents and a font and back cover. Such designs give elaborate information about the work done by him and pass on critical information about his skills and experience.
Portfolio Presentation and Organisation
The way a graphic design portfolio is presented and organized reflects the designer’s attention to detail, professionalism, and ability to communicate.
1. Layout and Presentation Skills
A strong Layout and Presentation Style can be demonstrated using:
- Cohesive Aesthetic
- Uniform use of colors, typography, and layout.
- The designer’s branding, such as a logo, color palette, and typography.
- Minimalist Approach
- Attention to Detail, from spacing and alignment to font choices and image quality
- Visual Hierarchy
- Prioritization of Content through size, color contrast, and placement.
- Balanced Layouts so that each project has enough space to stand out.
For example
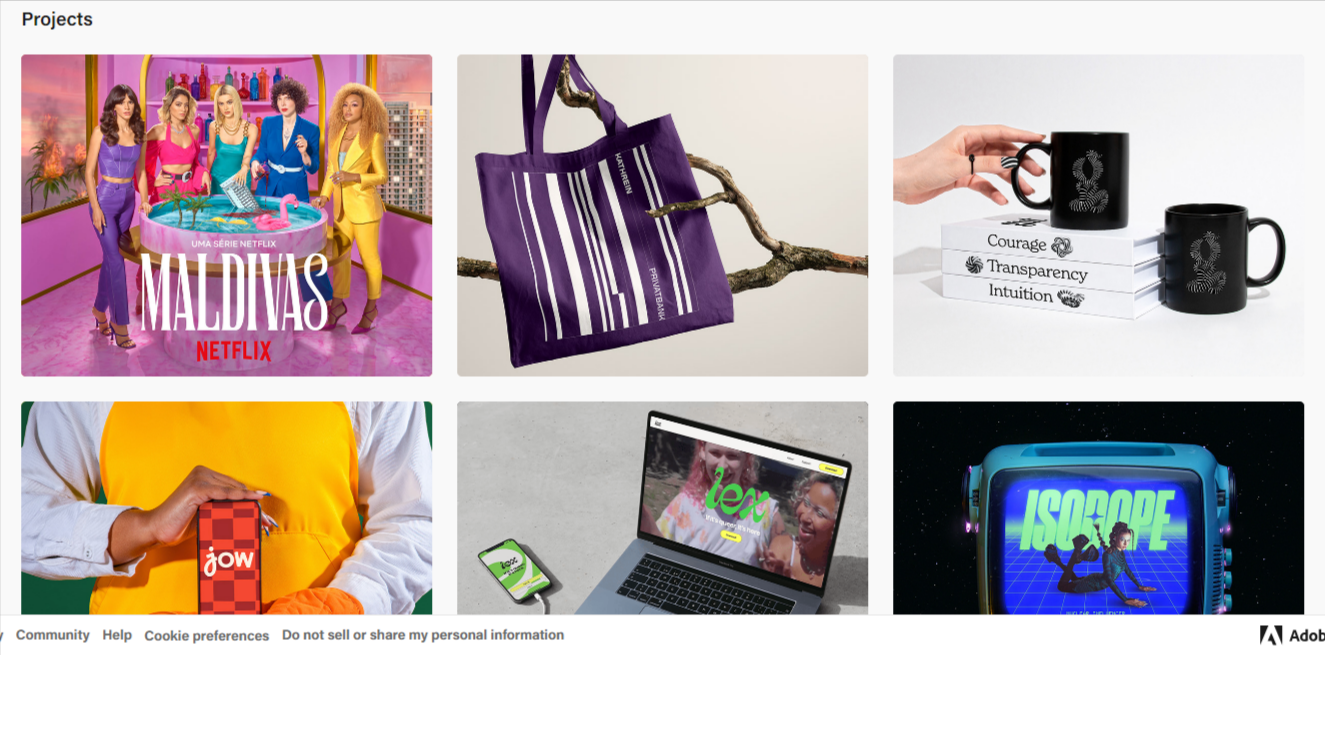
Jessica Walsh’s portfolio with eye-catching imagery and typographic finesse draws top clients like Apple, Benefit, and Levis.
2. Navigation and Accessibility of Portfolio Content
The portfolio should have an intuitive structure that is easy for viewers to navigate. It should have clear sections and well-designed navigation menus that are easy to find and use.
- The portfolio should be fully responsive and should function well on all devices.
- It should be able to open across different web browsers, include alt text for images to improve accessibility, and ensure that the text is readable.
- The portfolio must use optimized images and media files to ensure fast loading times.
- It should come with a search bar to help users find specific projects within the portfolio.
- The designer can also use tags and categories to organize content.
- Look out for interactive elements and prototypes to showcase UX/UI design.
For example:
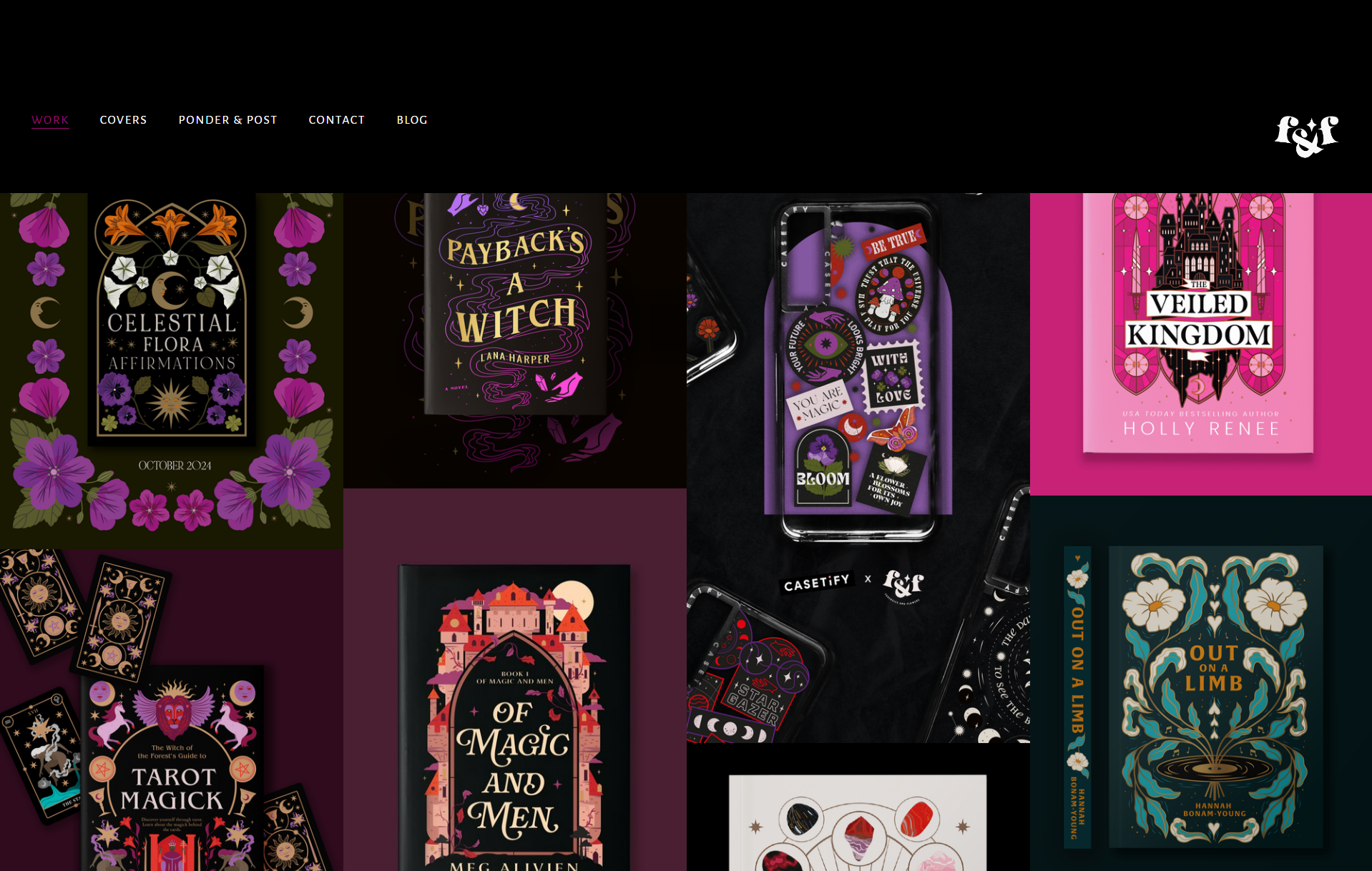
The Forensics & Flowers designer portfolio portrays a glimpse into dazzling designs, posters, and mockups that reflect the wow effects of his work.
Evaluation Techniques and Tips
Finally, when it comes to selecting from the best graphic design portfolios, you must use structured techniques and the right questions. Here are some best practices:
1. Comparative Analysis of Portfolios
- Compare the quality and creativity of the work to industry standards.
- Look for originality, innovation, and the ability to solve design problems creatively.
- Assess technical proficiency in design software, attention to detail, and execution of design principles.
- Compare the range of projects in different portfolios.
- Evaluate consistency in quality across all projects.
- Compare the visual presentation and organization of portfolios.
- Assess how easily you can navigate each portfolio.
Let us take Chelsea Cardinal’s portfolio as an example. Although it is text-centric, see how neatly it organizes projects, spacing, size, and color, creating a solid impression and being easy to navigate.

2. Asking Relevant Questions During Portfolio Review
When going through a portfolio review, you can ask some integral questions to the graphic designer like:
- What inspired the design decisions in this project?
- Can you walk me through your design process for this project?
- What challenges did you face during this project?
- How did you overcome them?
- How did you ensure the design met the client’s needs and goals?
- Which design tools and software did you use for this project?
- Can you explain any advanced techniques or methods used in this project?
- Do you have any feedback or testimonials from clients regarding this project?
- Is there anything you would do differently?
Conclusion
Following this guide can make your graphic designer selection easy. Evaluating a graphic designer’s portfolio requires attention to various key elements, which we have covered in this overview.
Assessing a graphic designer’s portfolio and aligning it with your hiring needs is significant. This evaluation will help you gauge design skills, creativity, technical proficiency, and professional collaboration. Most importantly, you must ensure that the designer fits well within your team and can contribute effectively to your projects.